
News
Pro . 03, 2024 19:11 Back to list
Citric Acid as an Effective Chelating Agent for Iron Management in Various Applications
The Role of Citric Acid as a Chelating Agent for Iron An In-Depth Analysis
Citric acid, a natural organic acid found in citrus fruits, has garnered increasing attention in various scientific and industrial fields due to its unique chemical properties. One of the most significant applications of citric acid is its function as a chelating agent, particularly in the sequestration of iron ions. This article delves into the mechanisms by which citric acid interacts with iron, the implications of this interaction, and its diverse applications.
Understanding Chelation
Chelation refers to the process by which a chelating agent forms multiple bonds with a single metal ion. This multi-point attachment stabilizes the metal ion, preventing it from participating in undesired chemical reactions. Iron, being a vital metal for various biological processes, can exist in multiple oxidation states, with ferric (Fe³⁺) and ferrous (Fe²⁺) ions being the most common. The proper management of iron in biological and environmental systems is crucial, as its mismanagement can lead to oxidative stress and other detrimental effects.
Mechanism of Citric Acid as a Chelating Agent
Citric acid contains three carboxylic acid groups and one hydroxyl group, allowing it to effectively form chelates with metal ions. The chelation of iron by citric acid typically occurs through the formation of a stable five-membered ring structure, which enhances the stability of the iron-citric acid complex. This coordination impedes iron’s ability to react with other substances, thus offering a means of regulating its bioavailability and reactivity.
When citric acid interacts with iron, the pH of the environment plays a vital role. In slightly acidic conditions, citric acid can effectively solubilize iron, making it more bioavailable for plant uptake in agricultural settings. Conversely, in alkaline conditions, iron tends to precipitate as insoluble oxides, making it unavailable to biological systems. Therefore, the chelation effect of citric acid is crucial in enhancing iron solubility under various environmental conditions.
citric acid chelating agent iron quotes
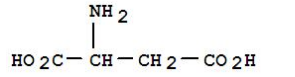
Applications of Citric Acid in Iron Chelation
1. Agriculture One of the most prominent uses of citric acid as a chelating agent is in agriculture. Iron deficiency is a common issue in crops, leading to chlorosis and reduced yields. The application of citric acid can improve iron availability in the soil, promoting healthy plant growth. This method is particularly useful in calcareous soils where iron is predominantly in an unavailable form.
2. Food Industry In the food industry, citric acid plays a dual role as both a preservative and a chelating agent. By binding free iron, it prevents the oxidative degradation of various nutrients and pigments, thereby maintaining the quality and flavor of food products. This application is especially significant in products where iron-induced oxidation can lead to rancidity.
3. Pharmaceuticals Citric acid's ability to chelate iron has potential applications in pharmaceuticals, particularly in the treatment of conditions such as hemochromatosis, a disorder characterized by excess iron accumulation in the body. By using citric acid to chelate excess iron, it may be possible to enhance iron excretion, thereby alleviating some of the symptoms associated with this condition.
4. Environmental Remediation Citric acid is also being explored for its role in environmental remediation. By chelating heavy metals, including iron, citric acid can help mobilize contaminants, aiding in their removal from polluted sites. Its biodegradable nature makes it an attractive candidate for green remediation techniques.
Conclusion
Citric acid serves as an essential chelating agent, particularly for iron, with far-reaching implications across various domains. Its ability to enhance iron solubility in agricultural settings bolsters plant health and productivity, while its applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries ensure product quality and therapeutic benefits. Moreover, in environmental contexts, citric acid can play a pivotal role in mitigating metal contaminants, promoting a greener approach to remediation. As research continues to unfold, the significance of citric acid in managing iron and other metal ions is only expected to grow, highlighting its versatility and importance in both natural and industrial ecosystems.
-
Polyaspartic Acid Salts in Agricultural Fertilizers: A Sustainable Solution
NewsJul.21,2025
-
OEM Chelating Agent Preservative Supplier & Manufacturer High-Quality Customized Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Potassium Chelating Agent Manufacturer - Custom Potassium Oxalate & Citrate Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Pentasodium DTPA Chelating Agent Supplier & Manufacturer High Purity & Cost-Effective Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Efficiency Chelated Trace Elements Fertilizer Bulk Supplier & Manufacturer Quotes
NewsJul.07,2025
-
High Quality K Formation for a Chelating Agent – Reliable Manufacturer & Supplier
NewsJul.07,2025
