
News
Čvc . 15, 2024 15:40 Back to list
Quotes on the effectiveness of chelating agents for lead detoxification and removal properties.
Chelating agents are chemical compounds that can form complexes with metal ions, holding them tightly and preventing their reactivity with other molecules. One of the most important applications of chelating agents is in the removal of heavy metal ions from contaminated water sources. Lead, in particular, is a highly toxic metal that can cause serious health issues when present in drinking water.
.
Furthermore, chelating agents are highly selective for specific metal ions, which means that they can target lead ions specifically without affecting other essential trace elements present in the water. This selectivity is crucial when treating contaminated water sources, as it ensures that the treatment process is both effective and safe for human consumption.
chelating agent lead quotes
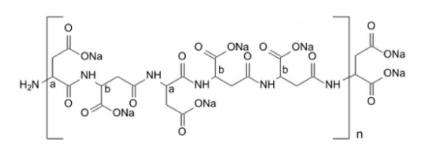
In addition to their efficacy in lead removal, chelating agents also offer environmental benefits. By preventing the reactivity of lead ions with other molecules, they reduce the risk of lead leaching into the environment and contaminating soil and groundwater. This can help to protect ecosystems and wildlife from the harmful effects of lead poisoning.
Overall, the use of chelating agents for lead removal in water treatment is a highly effective and sustainable option. As awareness of the dangers of lead contamination grows, the demand for safe and reliable methods of lead removal will only increase. Chelating agents offer a practical solution to this problem, providing a cost-effective and environmentally friendly way to ensure clean and safe drinking water for communities around the world.
In conclusion, chelating agents play a crucial role in the removal of lead from contaminated water sources. Their ability to form stable complexes with lead ions, their selectivity for specific metal ions, and their environmental benefits make them a valuable tool in the fight against lead pollution. As we continue to prioritize the health and safety of our water supplies, chelating agents will undoubtedly remain a key component of water treatment processes for years to come.
-
Polyaspartic Acid Salts in Agricultural Fertilizers: A Sustainable Solution
NewsJul.21,2025
-
OEM Chelating Agent Preservative Supplier & Manufacturer High-Quality Customized Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Potassium Chelating Agent Manufacturer - Custom Potassium Oxalate & Citrate Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Pentasodium DTPA Chelating Agent Supplier & Manufacturer High Purity & Cost-Effective Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Efficiency Chelated Trace Elements Fertilizer Bulk Supplier & Manufacturer Quotes
NewsJul.07,2025
-
High Quality K Formation for a Chelating Agent – Reliable Manufacturer & Supplier
NewsJul.07,2025
