
News
okt . 31, 2024 12:28 Back to list
OEM Calcium Ion Chelator for Enhanced Performance in Industrial Applications
The Role of OEM Calcium Ion Chelators in Biomedical Applications
Calcium ions (Ca²⁺) are essential signaling molecules in various biological processes, including muscle contraction, neurotransmitter release, and hormone secretion. However, excessive levels of calcium ions can lead to cellular dysfunction and contribute to various diseases. Therefore, the development and application of calcium ion chelators have gained significant attention in biomedical research and industry. Among the promising options available, OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) calcium ion chelators have emerged as vital tools in both clinical and research settings.
OEM calcium ion chelators are specially formulated compounds designed to bind to calcium ions, effectively removing them from biological systems or limiting their availability to cells. The importance of these chelators lies in their ability to modulate calcium levels in physiological and pathological situations, providing a pathway to therapeutic interventions in a range of conditions.
The Role of OEM Calcium Ion Chelators in Biomedical Applications
Another significant area where OEM calcium ion chelators are proving beneficial is in neurological research. Calcium ions play a pivotal role in neuronal excitability and neurotransmission; however, their dysregulation is linked to conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and epilepsy. By employing calcium ion chelators, researchers can investigate the intricate mechanisms by which calcium signaling contributes to neuronal health and disease. This knowledge can pave the way for innovative therapeutic approaches aimed at mitigating calcium-induced neurotoxicity.
oem calcium ion chelator
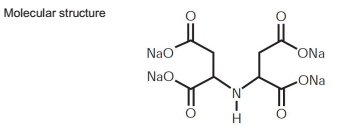
Furthermore, the use of OEM calcium ion chelators extends into the realm of cancer treatment. Certain cancers exhibit elevated calcium levels, which can promote tumor growth and metastasis. Studies have shown that calcium ion chelation may inhibit cancer cell proliferation and induce apoptosis, presenting a novel therapeutic strategy. As researchers continue to explore this avenue, the potential for OEM calcium ion chelators to serve as adjunct therapies in cancer treatment is becoming increasingly apparent.
In addition to their therapeutic roles, OEM calcium ion chelators are of great importance in laboratory settings. They are frequently employed in cell culture and biochemistry experiments to control calcium concentrations, ensuring that experimental conditions remain consistent and reliable. This is crucial for obtaining accurate results in studies focused on cell signaling, enzyme activity, and protein interactions.
Overall, OEM calcium ion chelators are versatile compounds with significant implications for both clinical applications and basic research. Their ability to modulate calcium levels provides a powerful tool for addressing a range of health issues associated with calcium dysregulation. As the understanding of calcium signaling pathways deepens, further innovations in OEM calcium ion chelator design and application are anticipated, paving the way for more effective treatments and findings in biomedical science. The ongoing research in this field highlights the importance of precise calcium management in promoting health and treating disease.
In conclusion, the role of OEM calcium ion chelators in biomedical applications cannot be underestimated. Their unique properties offer promising pathways for advancing healthcare and enhancing our understanding of calcium's multifaceted role in biology.
-
Polyaspartic Acid Salts in Agricultural Fertilizers: A Sustainable Solution
NewsJul.21,2025
-
OEM Chelating Agent Preservative Supplier & Manufacturer High-Quality Customized Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Potassium Chelating Agent Manufacturer - Custom Potassium Oxalate & Citrate Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Pentasodium DTPA Chelating Agent Supplier & Manufacturer High Purity & Cost-Effective Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Efficiency Chelated Trace Elements Fertilizer Bulk Supplier & Manufacturer Quotes
NewsJul.07,2025
-
High Quality K Formation for a Chelating Agent – Reliable Manufacturer & Supplier
NewsJul.07,2025
