
News
Jan . 25, 2025 23:04 Back to list
versene acid chelating agent factory
The realm of bifunctional chelating agents is rapidly evolving, garnering significant attention within various scientific and industrial sectors. These agents hold a unique position due to their dual functionality, playing a pivotal role in diverse applications, ranging from medical imaging to environmental remediation. Their innovation lies in their ability to bind selectively to metal ions through multiple coordination sites, setting them apart from traditional chelating agents.
New advancements continue to expand the potential uses of bifunctional chelating agents. Recent research has focused on developing agents with enhanced specificity and binding strength. Scientists are exploring novel synthetic pathways to create more robust agents capable of operating under extreme conditions. These innovations promise to extend their utility across a wider range of applications, from catalysis in chemical processes to advancements in nanotechnology. Investments in research and development are also driving the market, with companies recognizing the lucrative potential of these agents. Collaborations between academic institutions and private enterprises are fostering innovative solutions and accelerating the introduction of next-generation agents. This trend underscores a strong, ongoing commitment to exploring the full capabilities and applications of bifunctional chelating agents. Trustworthiness remains a cornerstone in the adoption and application of bifunctional chelating agents. Industry leaders prioritize transparency in their research and manufacturing processes, ensuring that their products meet the highest standards. Comprehensive testing and quality control measures are integral to maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of these agents, bolstering confidence amongst end-users and stakeholders alike. In conclusion, bifunctional chelating agents represent a dynamic and multifaceted field. Their proven benefits in medical, environmental, and industrial applications underscore their invaluable contribution to advancing technology and enhancing quality of life. As research continues to uncover new possibilities, these agents are poised to remain at the forefront of innovation, offering sustainable and effective solutions across multiple sectors.

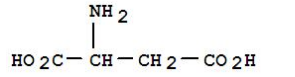
New advancements continue to expand the potential uses of bifunctional chelating agents. Recent research has focused on developing agents with enhanced specificity and binding strength. Scientists are exploring novel synthetic pathways to create more robust agents capable of operating under extreme conditions. These innovations promise to extend their utility across a wider range of applications, from catalysis in chemical processes to advancements in nanotechnology. Investments in research and development are also driving the market, with companies recognizing the lucrative potential of these agents. Collaborations between academic institutions and private enterprises are fostering innovative solutions and accelerating the introduction of next-generation agents. This trend underscores a strong, ongoing commitment to exploring the full capabilities and applications of bifunctional chelating agents. Trustworthiness remains a cornerstone in the adoption and application of bifunctional chelating agents. Industry leaders prioritize transparency in their research and manufacturing processes, ensuring that their products meet the highest standards. Comprehensive testing and quality control measures are integral to maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of these agents, bolstering confidence amongst end-users and stakeholders alike. In conclusion, bifunctional chelating agents represent a dynamic and multifaceted field. Their proven benefits in medical, environmental, and industrial applications underscore their invaluable contribution to advancing technology and enhancing quality of life. As research continues to uncover new possibilities, these agents are poised to remain at the forefront of innovation, offering sustainable and effective solutions across multiple sectors.
Latest news
-
Polyaspartic Acid Salts in Agricultural Fertilizers: A Sustainable Solution
NewsJul.21,2025
-
OEM Chelating Agent Preservative Supplier & Manufacturer High-Quality Customized Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Potassium Chelating Agent Manufacturer - Custom Potassium Oxalate & Citrate Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Pentasodium DTPA Chelating Agent Supplier & Manufacturer High Purity & Cost-Effective Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Efficiency Chelated Trace Elements Fertilizer Bulk Supplier & Manufacturer Quotes
NewsJul.07,2025
-
High Quality K Formation for a Chelating Agent – Reliable Manufacturer & Supplier
NewsJul.07,2025
