
News
Feb . 08, 2025 07:44 Back to list
High-performance set retarder for calcium sulfate(gypsum) Retarder - HN150P
Chelated fertilizers have been instrumental in transforming agricultural practices and boosting plant health. Understanding their meaning and application can guide growers towards more effective and sustainable farming methods. This article draws on expert knowledge and credible sources to explain the advantages, mechanisms, and expert recommendations for using chelated fertilizers.
Given their efficacy, it’s crucial to approach the use of chelated fertilizers with expert precision. Soil tests are recommended to determine existing nutrient levels before application. This prevents over-application, which can lead to nutrient imbalances or waste. Furthermore, selecting the correct chelate is essential. EDTA and DTPA are common chelating agents, each suited to specific soil pH ranges; EDTA is optimal for slightly acidic to neutral pH, while DTPA performs better in a moderately alkaline soil environment. In terms of environmental considerations, chelated fertilizers offer an eco-friendly solution. Their efficient nutrient delivery reduces the need for large fertilizer quantities, consequently minimizing runoff and potential waterway contamination. Agriculture experts advocate for their use as part of integrated nutrient management systems, which aim to improve yield and reduce environmental impact. This perspective is extensively supported by agricultural research institutions emphasizing sustainable practices. In conclusion, chelated fertilizers embody advanced agricultural technology by improving plant nutrient absorption and promoting sustainable farming. As specialists continue to research and optimize these compounds, they remain a cornerstone for both commercial agriculture and individual horticulture efforts. With careful application and adherence to expert recommendations, chelated fertilizers present a reliable path to healthier plant growth and enhanced ecological stewardship.

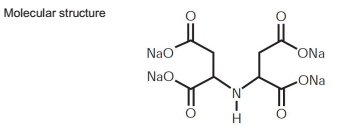
Given their efficacy, it’s crucial to approach the use of chelated fertilizers with expert precision. Soil tests are recommended to determine existing nutrient levels before application. This prevents over-application, which can lead to nutrient imbalances or waste. Furthermore, selecting the correct chelate is essential. EDTA and DTPA are common chelating agents, each suited to specific soil pH ranges; EDTA is optimal for slightly acidic to neutral pH, while DTPA performs better in a moderately alkaline soil environment. In terms of environmental considerations, chelated fertilizers offer an eco-friendly solution. Their efficient nutrient delivery reduces the need for large fertilizer quantities, consequently minimizing runoff and potential waterway contamination. Agriculture experts advocate for their use as part of integrated nutrient management systems, which aim to improve yield and reduce environmental impact. This perspective is extensively supported by agricultural research institutions emphasizing sustainable practices. In conclusion, chelated fertilizers embody advanced agricultural technology by improving plant nutrient absorption and promoting sustainable farming. As specialists continue to research and optimize these compounds, they remain a cornerstone for both commercial agriculture and individual horticulture efforts. With careful application and adherence to expert recommendations, chelated fertilizers present a reliable path to healthier plant growth and enhanced ecological stewardship.
Latest news
-
Polyaspartic Acid Salts in Agricultural Fertilizers: A Sustainable Solution
NewsJul.21,2025
-
OEM Chelating Agent Preservative Supplier & Manufacturer High-Quality Customized Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Potassium Chelating Agent Manufacturer - Custom Potassium Oxalate & Citrate Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Pentasodium DTPA Chelating Agent Supplier & Manufacturer High Purity & Cost-Effective Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Efficiency Chelated Trace Elements Fertilizer Bulk Supplier & Manufacturer Quotes
NewsJul.07,2025
-
High Quality K Formation for a Chelating Agent – Reliable Manufacturer & Supplier
NewsJul.07,2025
