
News
Dec . 09, 2024 22:49 Back to list
Current Prices for EDTA Chelated Zinc Fertilizer and Market Trends
Understanding the Price Dynamics of EDTA Chelated Zinc Fertilizer
In the world of agriculture, the role of micronutrients cannot be overstated. Among these, zinc is crucial for plant growth, influencing enzyme function, protein synthesis, and overall plant metabolism. One of the most effective forms of zinc fertilizer is EDTA chelated zinc, which enhances the bioavailability of zinc to plants. Understanding the price dynamics of EDTA chelated zinc fertilizer is essential for farmers, agronomists, and agricultural businesses alike.
What is EDTA Chelated Zinc Fertilizer?
EDTA or ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid is a chelating agent that binds to metal ions, making them more available to plants. This is particularly important in soils where zinc is present in forms that plants cannot absorb. By using EDTA chelated zinc, farmers can ensure that their crops receive an adequate supply of zinc, thus preventing deficiency symptoms such as stunted growth, leaf chlorosis, and reduced yield.
Factors Influencing Prices
The price of EDTA chelated zinc fertilizer is influenced by several factors
1. Raw Material Costs The primary components for producing zinc fertilizers include zinc oxide and the EDTA chelating agent. Fluctuations in the prices of these raw materials due to market demand, mining costs, or even geopolitical issues can significantly impact the final price of the fertilizer.
2. Manufacturing Process The production of EDTA chelated zinc is more complex than that of conventional zinc fertilizers. The manufacturing process involves additional steps to create the chelated form, which can lead to higher production costs. Facilities required for this process also contribute to the overall pricing structure.
edta chelated zinc fertilizer price
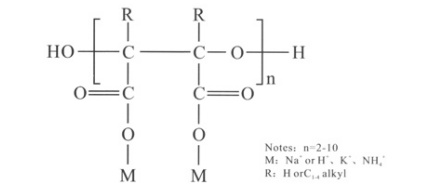
3. Market Demand The demand for EDTA chelated zinc fertilizer is driven by agricultural trends. With the growing emphasis on sustainable farming practices, there has been an increased focus on micronutrient supplementation. As farmers become more aware of the benefits of using chelated zinc, demand rises, potentially leading to price increases.
4. Seasonality Prices can be seasonal, with costs often rising before planting seasons when farmers stock up on fertilizers. This seasonal spike can be compounded by regional variations in agricultural practices and crop types that use zinc more heavily.
5. Supply Chain Dynamics Transportation costs significantly contribute to the final product price. Fluctuations in fuel prices and logistical challenges can affect the cost of getting the product from manufacturers to retailers, thereby influencing retail prices.
Current Market Trends
As of 2023, the market for EDTA chelated zinc fertilizer has seen notable trends. The push for precision farming and the adoption of technology in agriculture have led to increased adoption rates of micronutrient fertilizers, including chelated forms. Additionally, regions facing soil degradation and nutrient depletion have heightened the demand for effective fertilizer options, further impacting pricing.
International trade policies and tariffs also play a role in the pricing of agricultural inputs. Farmers in certain regions may face higher costs due to import duties on fertilizers produced overseas. As global supply chains stabilize post-pandemic, fluctuations in price may continue as markets seek a new equilibrium.
Conclusion
The price of EDTA chelated zinc fertilizer is influenced by a myriad of factors including raw material costs, manufacturing processes, market demand, and supply chain dynamics. For farmers, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions and optimizing their crop yields. As the agricultural landscape continues to evolve, keeping an eye on the trends in fertilizer pricing will remain essential for maximizing productivity and sustainability in farming practices. By appreciating the importance of micronutrients and the factors that drive their prices, stakeholders can better navigate the complexities of the agricultural marketplace.
-
Polyaspartic Acid Salts in Agricultural Fertilizers: A Sustainable Solution
NewsJul.21,2025
-
OEM Chelating Agent Preservative Supplier & Manufacturer High-Quality Customized Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Potassium Chelating Agent Manufacturer - Custom Potassium Oxalate & Citrate Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Pentasodium DTPA Chelating Agent Supplier & Manufacturer High Purity & Cost-Effective Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Efficiency Chelated Trace Elements Fertilizer Bulk Supplier & Manufacturer Quotes
NewsJul.07,2025
-
High Quality K Formation for a Chelating Agent – Reliable Manufacturer & Supplier
NewsJul.07,2025
