
News
Nov . 10, 2024 12:30 Back to list
Effective Chelating Agents for Enhancing Food Preservation and Safety
The Role of High-Quality Chelating Agents in Food Preservation
Food preservation is an essential aspect of ensuring food safety, extending shelf life, and maintaining nutritional quality in our diets. Among the various methods employed to preserve food, the use of chelating agents has gained attention for their effectiveness and versatility. Chelating agents, or chelators, are compounds that can form stable complexes with metal ions, thereby inhibiting their reactivity in food systems. This article explores the importance of high-quality chelating agents in food preservation and their contributions to enhancing food safety.
Understanding Chelating Agents
Chelating agents are organic compounds that can bind to metal ions, effectively removing them from a solution or matrix. Common metals that chelators target include iron, copper, and zinc, which can catalyze undesirable reactions in food products. For instance, iron can promote oxidative reactions that lead to rancidity, discoloration, and loss of nutritional value. By binding to these metal ions, chelating agents can stabilize the food product, thus preserving its quality over time.
Mechanisms of Action
The primary function of chelating agents in food preservation is to prevent oxidative spoilage. Oxidation can result in the degradation of vitamins, fats, and proteins, leading to off-flavors and microbial growth. The chelators work by sequestering metal ions that facilitate oxidative reactions, thereby slowing down the spoilage process. Furthermore, these agents can also enhance the solubility of certain nutrients, improving their bioavailability and contributing to the overall health benefits of preserved foods.
Types of Chelating Agents
Several types of chelating agents are utilized in food preservation, each with unique properties and applications. Among the most common are
1. Citric Acid A naturally occurring organic acid, citric acid is widely used in the food industry as a preservative and flavor enhancer. It effectively chelates metal ions, thus reducing their reactivity and preventing oxidization.
2. EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid) This synthetic compound is a powerful chelating agent that can bind to a variety of metal ions. EDTA is frequently used in canned foods and beverages to maintain color and flavor quality.
high quality chelating agent food preservation
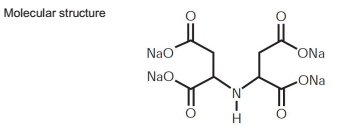
3. Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) Besides being a vital nutrient, ascorbic acid also acts as a natural chelator. It protects food from oxidation by binding with metal ions and reducing their pro-oxidative effects.
4. Phosphates These compounds are often used in processed meats and seafood. They not only act as chelators but also improve texture and moisture retention.
Benefits of High-Quality Chelating Agents
The use of high-quality chelating agents in food preservation offers several advantages
- Enhanced Shelf Life By effectively sequestering harmful metal ions, chelators help extend the shelf life of food products, reducing food waste and improving economic efficiency for producers.
- Improved Food Safety High-quality chelating agents can minimize the risk of foodborne pathogens by maintaining the integrity of food products and preventing spoilage.
- Nutritional Retention Chelators help retain vitamins and nutrients in foods by mitigating oxidative damage, thereby ensuring consumers receive maximum nutritional benefits from preserved products.
- Natural Alternatives Many high-quality chelating agents are derived from natural sources, appealing to health-conscious consumers seeking clean-label products.
Conclusion
In summary, high-quality chelating agents play a crucial role in modern food preservation. By effectively binding to metal ions and preventing oxidative reactions, these agents help maintain the quality, safety, and nutritional value of various food products. As consumer awareness of food safety and health continues to grow, the importance of selecting effective and safe chelating agents in food processing will undoubtedly remain a significant focus for the food industry. Embracing the benefits of chelation not only serves the interests of manufacturers but also provides consumers with safer, fresher, and more nutritious food options.
-
Polyaspartic Acid Salts in Agricultural Fertilizers: A Sustainable Solution
NewsJul.21,2025
-
OEM Chelating Agent Preservative Supplier & Manufacturer High-Quality Customized Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Potassium Chelating Agent Manufacturer - Custom Potassium Oxalate & Citrate Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Pentasodium DTPA Chelating Agent Supplier & Manufacturer High Purity & Cost-Effective Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Efficiency Chelated Trace Elements Fertilizer Bulk Supplier & Manufacturer Quotes
NewsJul.07,2025
-
High Quality K Formation for a Chelating Agent – Reliable Manufacturer & Supplier
NewsJul.07,2025
