
News
Sep . 01, 2024 11:02 Back to list
oem edta sebagai chelating agent
The Role of OEM EDTA as a Chelating Agent
Chelating agents play a vital role in various industrial, agricultural, and environmental applications. One such agent that has garnered attention is Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), particularly in its OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) form. This article explores the significance of EDTA as a chelating agent, its mechanisms, applications, and advantages.
The Role of OEM EDTA as a Chelating Agent
In agriculture, EDTA is often used to improve the bioavailability of essential micronutrients such as iron, zinc, and manganese. Many soils contain these nutrients, but they may not be readily available for plant uptake due to their inherent chemical forms. By chelating these metal ions, EDTA enhances their solubility and transportability, allowing plants to absorb them more efficiently. This leads to improved plant health, better yield, and higher-quality crops.
oem edta sebagai chelating agent
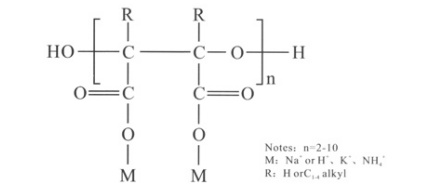
In industrial applications, OEM EDTA serves as a critical component in cleaning products, where it helps in the removal of calcium, magnesium, and other hardness-causing ions from water. By binding with these metal ions, EDTA prevents scale formation and improves the effectiveness of detergents and surfactants. Its ability to soften water is particularly important in processes such as textile manufacturing, paper production, and metal finishing.
Moreover, EDTA's chelating properties extend to environmental remediation. In contaminated sites, heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, and mercury pose significant risks to human health and ecosystems. EDTA can immobilize these toxic metals, making them less bioavailable and reducing their harmful effects. This application is crucial in developing strategies for soil and water decontamination, supporting cleaner and safer environments.
However, the use of EDTA is not without controversy. While it is highly effective in metal ion chelation, concerns have been raised regarding its environmental impact. Once chelated, the metal-EDTA complexes can persist in ecosystems, leading to potential bioaccumulation and adverse effects on aquatic life. Consequently, researchers are exploring biodegradable alternatives to EDTA that offer similar benefits without the long-term drawbacks.
In conclusion, OEM EDTA is a versatile and efficient chelating agent with a broad spectrum of applications across agriculture, industry, and environmental science. Its ability to improve nutrient availability in soils, enhance cleaning processes, and aid in environmental remediation reflects its importance in modern practices. However, as with any chemical agent, it is crucial to weigh its effectiveness against its environmental implications. Continued research into safer alternatives will be essential to ensure sustainable use while maximizing the benefits that EDTA can provide. In navigating these challenges, we can harness the power of chelation to benefit agriculture, industry, and environmental health responsibly.
-
Polyaspartic Acid Salts in Agricultural Fertilizers: A Sustainable Solution
NewsJul.21,2025
-
OEM Chelating Agent Preservative Supplier & Manufacturer High-Quality Customized Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Potassium Chelating Agent Manufacturer - Custom Potassium Oxalate & Citrate Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Pentasodium DTPA Chelating Agent Supplier & Manufacturer High Purity & Cost-Effective Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Efficiency Chelated Trace Elements Fertilizer Bulk Supplier & Manufacturer Quotes
NewsJul.07,2025
-
High Quality K Formation for a Chelating Agent – Reliable Manufacturer & Supplier
NewsJul.07,2025
