
News
Nov . 27, 2024 01:45 Back to list
Biodegradation of AES Chelant and Its Environmental Impact Assessment
Biodegradation of AES Chelants An Overview
As environmental concerns continue to grow, the need for sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives in various industrial processes has led to increasing focus on biodegradable agents. Among these agents, alkyl ether sulfonate (AES) chelants are noteworthy for their application in various sectors, including agriculture, cleaning, and pharmaceuticals. Understanding the biodegradation of these chelants is crucial in assessing their environmental impact and developing more sustainable practices.
AES chelants, derived from natural fatty alcohols, are surfactants known for their ability to bind with metal ions, which enhances the cleaning capabilities of products that contain them. They are commonly used in formulations for household cleaners, detergents, and industrial applications due to their effectiveness and relatively low toxicity. However, their persistence in the environment raises concerns about long-term ecological effects, particularly when they enter waterways and soil systems.
Biodegradation of AES Chelants An Overview
Research indicates that the biodegradation of AES chelants occurs through two primary pathways oxidation and hydrolysis. During oxidation, microorganisms utilize oxygen to break down the alkyl chain of the AES compounds, leading to the formation of smaller, more biodegradable products. Hydrolysis, on the other hand, involves the reaction of the chelant with water, leading to the release of metal ions and other byproducts. These processes are influenced by factors such as temperature, pH, and nutrient availability.
biodegradation of aes chelant quotes
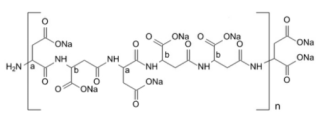
One of the critical advantages of AES chelants is their potential for rapid biodegradation under aerobic conditions. Various studies highlight that under optimal conditions, a significant percentage of AES can be degraded within days to weeks. For instance, laboratory experiments have demonstrated that microorganisms capable of utilizing AES chelants can reduce their concentration by over 90% in as little as 14 days in well-aerated environments. This rapid degradation is a positive attribute, suggesting that when introduced into the environment in controlled doses, the impact of these chelants can be minimized.
Moreover, the presence of specific microorganisms plays a crucial role in this biodegradation process. Microbial consortia, particularly those enriched in bioremediation studies, have shown enhanced capabilities to degrade AES chelants. The discovery of effective microbial strains offers an innovative approach for developing bioremediation strategies, which could mitigate the environmental impact of these chemicals in soil and water systems.
Furthermore, the use of natural and engineered microbial strains raises questions about the long-term sustainability and effectiveness of biodegradation processes. While certain microbes can effectively degrade AES chelants, the ecological balance must be considered to avoid unintended consequences in microbial communities or the broader environment.
In conclusion, the biodegradation of AES chelants is a promising area of research with significant implications for environmental sustainability. Ongoing studies aim to better understand the mechanisms involved and to optimize conditions for effective biodegradation. As industries seek to adopt greener alternatives, the role of biodegradable chelants like AES becomes increasingly essential. By advancing our knowledge in this field, we can work towards safer, more environmentally friendly practices that contribute to the protection of our ecosystems. As we move forward, it is vital to maintain a balance between industrial needs and ecological integrity, ensuring a healthier planet for future generations.
-
Polyaspartic Acid Salts in Agricultural Fertilizers: A Sustainable Solution
NewsJul.21,2025
-
OEM Chelating Agent Preservative Supplier & Manufacturer High-Quality Customized Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Potassium Chelating Agent Manufacturer - Custom Potassium Oxalate & Citrate Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Pentasodium DTPA Chelating Agent Supplier & Manufacturer High Purity & Cost-Effective Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Efficiency Chelated Trace Elements Fertilizer Bulk Supplier & Manufacturer Quotes
NewsJul.07,2025
-
High Quality K Formation for a Chelating Agent – Reliable Manufacturer & Supplier
NewsJul.07,2025
