
News
okt . 21, 2024 23:38 Back to list
Development of Tailored Chelating Agents for Enhanced Iron Absorption and Utilization
Custom Chelating Agents for Iron Enhancing Bioavailability and Utility
Iron is an essential nutrient that plays a pivotal role in various biological processes, including oxygen transport, energy production, and immune function. However, despite its abundance in nature, iron deficiency remains a prevalent issue worldwide, particularly in populations with limited access to diverse diets. To combat this challenge, researchers and nutritionists have turned their attention to custom chelating agents designed to improve the bioavailability of iron, making it more accessible for physiological use.
Understanding Chelation
Chelation is a chemical process in which a molecule, known as a chelator, binds to a metal ion, forming a stable complex. This process is crucial in various fields, including medicine, agriculture, and food science. In the context of iron, chelation enhances solubility and prevents precipitation, allowing for more efficient absorption in biological systems. Conventional chelating agents, such as EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) and citrate, have long been used to facilitate iron availability. However, these agents often lack specificity and can lead to undesirable interactions with other nutrients or contaminants.
Custom Chelating Agents A Tailored Approach
The development of custom chelating agents for iron represents a significant advancement in nutritional science. These agents are designed with specific characteristics to enhance their binding affinity for iron while minimizing interference with other biological processes. The custom design allows for the consideration of factors such as pH stability, binding strength, and selectivity towards ferric or ferrous ions.
One of the primary benefits of custom chelating agents is their potential to improve iron bioavailability in various food systems. For instance, many foods contain phytates and polyphenols, which can inhibit iron absorption. By employing custom chelators that can effectively bind with these inhibitors, researchers can enhance the overall iron bioavailability of these foods. This is particularly important in developing fortified foods targeting populations at risk of iron deficiency.
Mechanisms of Action
custom chelating agent for iron
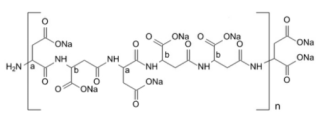
The mechanism by which chelating agents enhance iron availability can be understood through several interrelated processes. Firstly, custom chelators may facilitate the solubilization of iron, transforming it into a form that is more readily absorbed by the intestines. This is achieved through the formation of stable, water-soluble complexes that effectively “shield” the iron from interactions that would render it insoluble.
Secondly, custom chelors can modulate the release of iron in the gastrointestinal tract. By controlling the pH-dependent stability of these complexes, chelators can ensure that iron is released at optimal sites in the intestine, where absorption efficiency is maximized.
Finally, custom chelating agents can also interact with specific transport proteins, enhancing the uptake of iron by enterocytes (intestinal cells). Over time, this could lead to better overall iron status in individuals who consume such fortified products.
Applications in Food and Nutrition
The application of custom chelating agents is broad-ranging. In the food industry, these agents can be integrated into fortified products such as cereals, dairy, and beverages. By ensuring that these products contain bioavailable forms of iron, manufacturers can help combat iron deficiency in susceptible populations, including children and pregnant women.
Moreover, in pharmaceuticals, custom chelators can be utilized in iron supplements designed for individuals who require additional iron but face absorption challenges due to dietary composition or clinical conditions. This custom approach holds the promise of reducing gastrointestinal side effects commonly associated with traditional iron supplements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the development of custom chelating agents for iron represents a promising avenue for addressing iron deficiency and improving nutritional outcomes. By enhancing iron bioavailability through tailored interventions, researchers and industry practitioners can make strides toward mitigating this widespread public health issue. Continued research and innovation in this field will be essential to develop even more effective solutions, ultimately contributing to enhanced health and wellbeing for populations around the globe. As we continue to explore the possibilities of custom chelation technology, the potential for improving iron nutrition looks more promising than ever.
-
Polyaspartic Acid Salts in Agricultural Fertilizers: A Sustainable Solution
NewsJul.21,2025
-
OEM Chelating Agent Preservative Supplier & Manufacturer High-Quality Customized Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Potassium Chelating Agent Manufacturer - Custom Potassium Oxalate & Citrate Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Pentasodium DTPA Chelating Agent Supplier & Manufacturer High Purity & Cost-Effective Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Efficiency Chelated Trace Elements Fertilizer Bulk Supplier & Manufacturer Quotes
NewsJul.07,2025
-
High Quality K Formation for a Chelating Agent – Reliable Manufacturer & Supplier
NewsJul.07,2025
