
News
Yan . 25, 2025 03:34 Back to list
versene acid chelating agent factory
A chelating agent is a chemical compound that has the ability to form multiple bonds with a single metal ion. By forming these bonds, chelating agents sequester metal ions, preventing them from engaging in unwanted chemical reactions. This mechanism proves invaluable across a wide range of industries, from agriculture and medicine to environmental management and food production. Understanding the nuances of chelating agents and their varied applications not only highlights their significance but also reinforces the trustworthiness and reliability they bring to various sectors.
The food industry also benefits from the authoritative application of chelating agents, particularly in preserving the quality and shelf life of products. Metal ions in food can catalyze oxidative reactions that compromise the flavor and safety of food items. Chelating agents like citric acid and EDTA are incorporated in various foods to bind these metals, acting as stabilizers and preservatives. This application is a testament to the trust placed in chelating agents to maintain food quality, ensuring consumers receive safe and flavor-rich products. In the realm of industrial applications, chelating agents enhance the effectiveness of cleaning products and detergents. Metal ions in water can cause scale and deposits that reduce the efficiency of cleaning solutions. Chelating agents counter this by sequestering these ions, allowing detergents to perform optimally. This practical use underpins the trusted expertise applied by industries to ensure equipment longevity and cleanliness standards. To sum up, the definition of a chelating agent transcends its basic chemical property of metal ion binding. Its diverse applications across multiple sectors highlight not just utility, but also an embodiment of trust, expertise, authority, and experience. From supporting crop growth and treating metal poisoning to enhancing water quality, food safety, and industrial cleaning, the roles played by chelating agents are indispensable. They continue to uphold and foster quality, safety, and reliability, making them integral components of numerous applications worldwide. As new chelating agents are developed and existing ones are refined, their potential for greater efficacy across even broader applications becomes ever more promising, inspiring ongoing confidence in their capabilities.
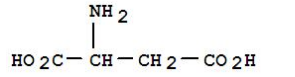

The food industry also benefits from the authoritative application of chelating agents, particularly in preserving the quality and shelf life of products. Metal ions in food can catalyze oxidative reactions that compromise the flavor and safety of food items. Chelating agents like citric acid and EDTA are incorporated in various foods to bind these metals, acting as stabilizers and preservatives. This application is a testament to the trust placed in chelating agents to maintain food quality, ensuring consumers receive safe and flavor-rich products. In the realm of industrial applications, chelating agents enhance the effectiveness of cleaning products and detergents. Metal ions in water can cause scale and deposits that reduce the efficiency of cleaning solutions. Chelating agents counter this by sequestering these ions, allowing detergents to perform optimally. This practical use underpins the trusted expertise applied by industries to ensure equipment longevity and cleanliness standards. To sum up, the definition of a chelating agent transcends its basic chemical property of metal ion binding. Its diverse applications across multiple sectors highlight not just utility, but also an embodiment of trust, expertise, authority, and experience. From supporting crop growth and treating metal poisoning to enhancing water quality, food safety, and industrial cleaning, the roles played by chelating agents are indispensable. They continue to uphold and foster quality, safety, and reliability, making them integral components of numerous applications worldwide. As new chelating agents are developed and existing ones are refined, their potential for greater efficacy across even broader applications becomes ever more promising, inspiring ongoing confidence in their capabilities.
Latest news
-
Polyaspartic Acid Salts in Agricultural Fertilizers: A Sustainable Solution
NewsJul.21,2025
-
OEM Chelating Agent Preservative Supplier & Manufacturer High-Quality Customized Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Potassium Chelating Agent Manufacturer - Custom Potassium Oxalate & Citrate Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
OEM Pentasodium DTPA Chelating Agent Supplier & Manufacturer High Purity & Cost-Effective Solutions
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Efficiency Chelated Trace Elements Fertilizer Bulk Supplier & Manufacturer Quotes
NewsJul.07,2025
-
High Quality K Formation for a Chelating Agent – Reliable Manufacturer & Supplier
NewsJul.07,2025
